What is the Endocannabinoid System & What Does It Do?
September 08, 2025
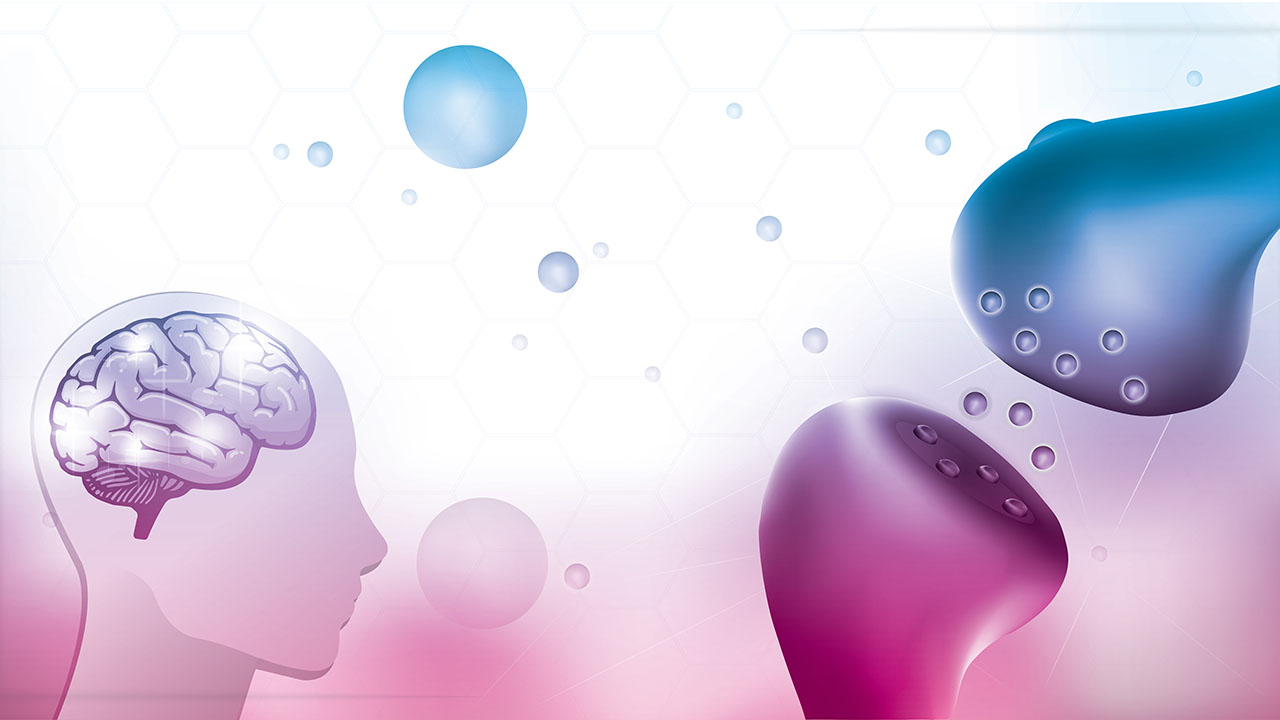
Ever wonder why cannabis affects everyone differently? The answer lies in your unique endocannabinoid system (ECS)—a network of messengers and receptors in your body that not only shapes your cannabis experience but also plays a key role in maintaining your overall balance and well-being. This intricate signaling system is full of complexities that researchers are only just starting to understand, but we’re here to cover where the science is at—and where it still has to go.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system, or endogenous cannabinoid system (ECS), is a complex messaging network that spans the entire body. It’s responsible for maintaining our internal physical balance, or “homeostasis.” When you feel hot, hungry, or tired, the endocannabinoid system springs into action to right whatever is wrong.1
The ECS consists of endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes, all working together to produce a variety of bodily processes—everything from temperature regulation to learning and memory. If there is a physical function critical to both our day-to-day and our survival, chances are good the endocannabinoid system has something to do with it.1
The endocannabinoid system is a recent discovery, as recent as 1988, so there’s still much about it we have yet to understand.2 We do know that endocannabinoid receptors appear nearly everywhere in the body—mostly in the brain and spinal cord, but also in the skin, muscles, and many organs. And we know that cannabis compounds—cannabinoids—can wield this system the same way our own homegrown endocannabinoids do (this is how the ECS was discovered, after all).
How Does the Endocannabinoid System Work?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) functions much like a lock-and-key mechanism and consists of three essential parts:
- Endocannabinoids: Naturally occurring compounds made inside the body that help regulate our internal balance.
- Endocannabinoid receptors (CB1 & CB2): Located throughout the body, these receptors interact with endocannabinoids to trigger physiological responses.
- Enzymes: Responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once their work is done.
The endocannabinoid receptors act as the locks, while endocannabinoids serve as the keys. When your body experiences an imbalance—whether from temperature changes, stress, or hunger—it produces endocannabinoids. These molecules travel through the body, binding to receptors and “unlocking” specific processes that help restore balance to your body. Once balance is reached, metabolic enzymes move in to break down endocannabinoids before they can push that balance too far in the other direction.3
Endocannabinoids
When we say endocannabinoids, we mean the molecular messengers made within our bodies (“endo-” means within). They’re technically neurotransmitters, but differ slightly because of their fatty composition. Endocannabinoids are not to be confused with phytocannabinoids, or the cannabinoids made by the cannabis plant (“phyto-” means plant). So far, researchers have identified two main endocannabinoids: anandamide (named for the Sanskrit word for bliss) and 2-AG (shorthand for 2-arachidonoyl glycerol). When something happens that requires our body’s response, it creates these endocannabinoids that then “unlock” or bind to endocannabinoid receptors, which help our body adjust to whatever situation we’re facing.1
Endocannabinoid Receptors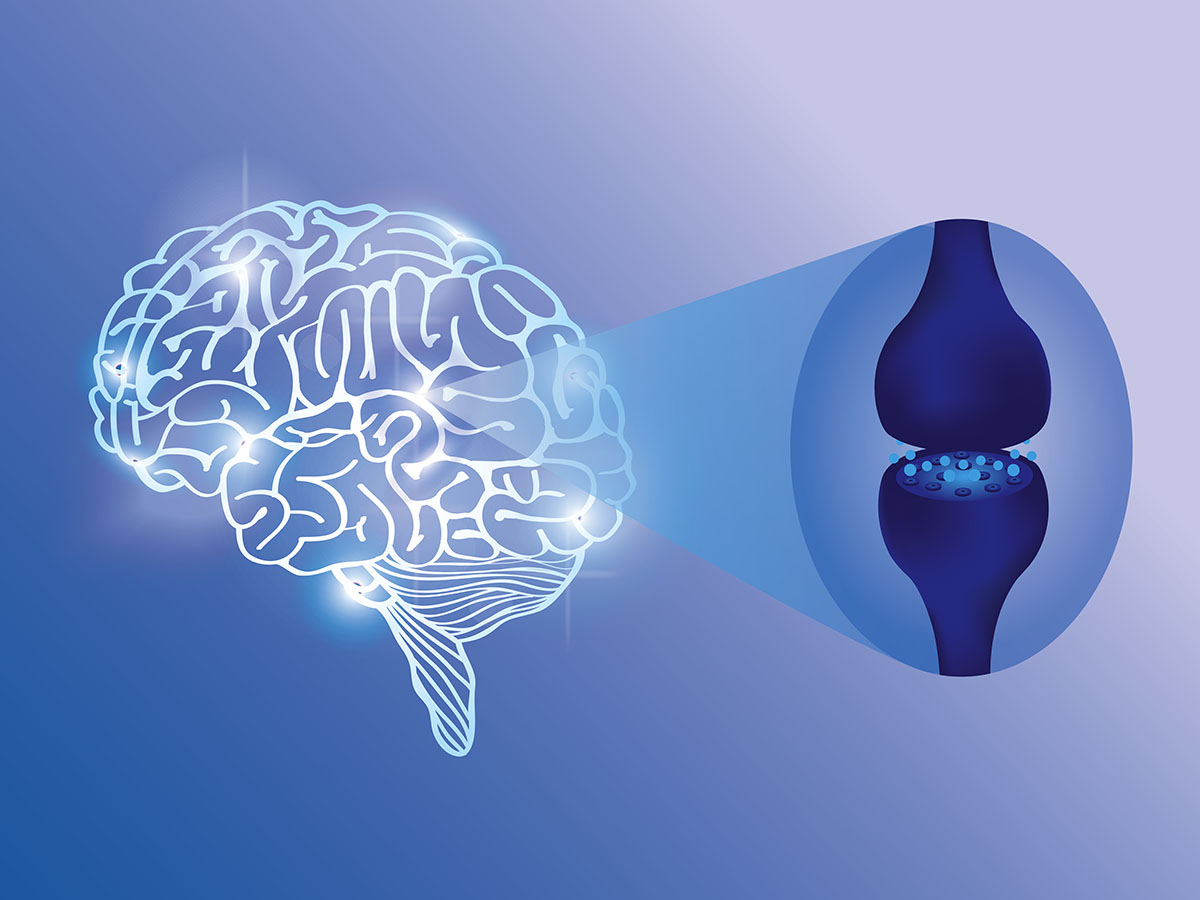
You’ll find endocannabinoid receptors on the surfaces of cells throughout your entire body. These receptors are activated when endocannabinoids bind to them, triggering physiological responses.3 A simple example is body temperature regulation—when you overheat, your body releases endocannabinoids that bind to receptors in your skin, triggering the sweat process to cool you down. So far, researchers have identified two primary cannabinoid receptors:4
- Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R): Found primarily in the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, the CB1 receptor is the most abundant receptor type in the brain and plays a key role in modulating the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
- Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R): While some CB2 receptors are present in the central nervous system, they’re primarily located in the immune system, where they help regulate inflammation and immune responses.
Enzymes
So what about the enzymes? You can think of the enzymes in the ECS as the clean-up crew. Once endocannabinoids have done their job and activated the proper endocannabinoid receptors to prompt the necessary response in our body, it’s time for them to go. Metabolic enzymes come along and break down the endocannabinoids. This is so they don’t overcorrect the problem, and put the body out of balance in the other direction.5
What Does the Endocannabinoid System Do?
The endocannabinoid system is our body’s natural way of regulating itself and responding to both internal and external influences. This could involve every physical process we’re capable of. Each passing year contributes to a growing body of research demonstrating the multitude of processes the endocannabinoid system is involved in. It’s very exciting for cannabis enthusiasts, but the versatility of the ECS also holds significant promise to leverage in the treatment of several conditions, including chronic pain and PTSD.1 Of course, more research is needed.
So far, we’ve found evidence that the endocannabinoid system could have a hand in:2
- Appetite, metabolism, and digestion
- Cognition, learning, and memory
- Fertility and pregnancy
- Immune system function and inflammation
- Mood regulation
- Pain perception
- Sleep, including circadian rhythms and REM cycle
- Temperature control
If you’re ever struggling to remember exactly what the endocannabinoid system does, just remember these five words that can help to sum it all up: eat, sleep, relax, protect, and forget.3
How Do THC and CBD Interact with the ECS?
The endocannabinoid system is the reason we feel the psychoactive and physical effects of cannabis. Phytocannabinoids, like THC and CBD, share a strikingly similar molecular structure to our own endocannabinoids, meaning they can bind to endocannabinoid receptors in the same way. This means they hold the power to activate the physiological processes of the endocannabinoid system. This is why we associate several physical sensations with cannabis, like tingling skin, “the munchies,” and fatigue.
Two of the most famous phytocannabinoids are THC and CBD, but there are hundreds more that exist within the cannabis plant family, and even some that have been found in other plant species.6 Because researchers know the ECS plays such a fundamental role in important functions within our bodies, they hypothesize that we could potentially use cannabis to cause certain reactions in the ECS.1
THC
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is known as the psychoactive phytocannabinoid—it’s the compound responsible for creating that “high” feeling we associate with cannabis consumption.6 This is because THC, while it binds to both endocannabinoid receptors, is especially partial to CB1—the most abundant endocannabinoid receptor in the brain.7 THC binding with CB1 is what triggers these psychoactive effects. It’s also why researchers are trying to understand if THC could be an important tool in treating conditions that affect memory, mood, motor control, and more.7

CBD
Unlike THC, CBD (cannabidiol) doesn't appear to bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors. Instead, CBD seems to prolong the presence of endocannabinoids in the body by slowing their breakdown, allowing them to interact with receptors for a longer period. This extended interaction amplifies the body’s natural response to phytocannabinoids. In addition, CBD may affect the CB1 receptor by dulling its signal.5 This is why some marijuana consumers insist that strains with CBD tend to create a more moderate experience compared to products with high levels of THC and minimal (if any) CBD.8 While CBD may not specifically bind to the CB2 receptor, it does seem to amplify the CB2 receptor’s signal. Research indicates CB2 receptors help regulate things like inflammation and immune responses within the body, so it’s possible CBD could, one day, be a catalyst in the treatment of inflammatory conditions.5 The research on the use of THC and CBD for the treatment of various ailments is optimistic, but science is still a long way from fully understanding how these phytocannabinoids influence the body.
What is the Entourage Effect?
When it comes to how the body processes and reacts to cannabis, the entourage effect and the endocannabinoid system work hand-in-hand. The entourage effect is a theory that all of the compounds within cannabis—phytocannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids—produce a stronger effect when consumed together rather than individually. This means that full-spectrum products, or products specifically manufactured to retain the highest amount of original compounds, could change or enhance the way the compounds in cannabis interact with the endocannabinoid system.8
Endocannabinoid System FAQs
There’s a lot of science involved with the endocannabinoid system, and research is ongoing. So it’s no surprise that we get a lot of questions about the ECS. Here are some of our most common questions and their answers:
Does THC affect the endocannabinoid system?
Yes, THC’s effect on CB1 receptors of the endocannabinoid system is what creates the psychoactive experience the cannabinoid is known for.6
Does CBD affect the endocannabinoid system?
Yes, CBD affects the endocannabinoid system in three ways: it interferes with signals sent to CB1 receptors, it amplifies signals sent to CB2 receptors, and it may also increase the time our naturally occurring endocannabinoids can interact with cells in our body.5
What else stimulates the endocannabinoid system?
Foods and activities that reduce your stress levels or improve your mood are likely doing so by interacting with your endocannabinoid system. You can eat foods rich in omega-3 and -6 oils, indulge in chocolate (especially dark chocolate), sip on certain teas, exercise, and even just hang out with friends.9 In general, if it helps your body get the nutrients it needs, relaxes you, or makes you happy, there’s a good chance it’s helping to stimulate your endocannabinoid system.
Does the endocannabinoid system only work with cannabis?
No, our endocannabinoid system exists and functions independent of cannabis. It’s named this way because cannabis led to its discovery. And while cannabis compounds are capable of interacting with the ECS, they are not needed for the ECS to work. Other external factors, like those mentioned above, can stimulate and affect the endocannabinoid system.
When was the endocannabinoid system discovered?
The discovery of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) unfolded over several years. In 1988, scientists identified the presence of cannabinoid receptors, marking a major breakthrough. Just a few years later, in 1992, researchers isolated anandamide, the first known endocannabinoid. From there, discoveries accelerated, soon revealing additional receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes.10
Who discovered the endocannabinoid system?
Several research labs were at the forefront of cannabis research. In 1988, Allyn Howlett’s lab at Saint Louis University identified the first cannabinoid receptors. Just a few years later, in 1992, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam and his lab team isolated anandamide, the first known endocannabinoid. These milestones set off a domino effect, leading to further discoveries that deepened our understanding of the endocannabinoid system and its role in the body.10
Learning About The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system is more than just a biological network—it’s a key player in how we experience cannabis and maintain balance in our daily lives. By understanding how cannabinoids interact with the ECS, we gain deeper insight into how cannabis can influence mood, pain relief, relaxation, and overall well-being. Now that you know more about the ECS, why not put that knowledge into action? Explore our menu, visit one of our locations, and find the perfect strain or product to experience the entourage effect firsthand. Whether you're seeking relaxation, creativity, or pain relief, the ECS is working behind the scenes to enhance your experience—so dive in and discover what works best for you!
Sources:
1. “The endocannabinoid system: Essential and mysterious,” Harvard Health Publishing, https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-endocannabinoid-system-essential-and-mysterious-202108112569
2. “The Endocannabinoid System: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Various Diseases,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, August 31, 2021, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8430969/
3. “What is the Endocannabinoid System and How Does Cannabis Affect It?” GoodRx, October 24, 2023, https://www.goodrx.com/classes/cannabinoids/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system
4. “A Simple Guide to the Endocannabinoid System,” Healthline, May 17, 2019, https://www.healthline.com/health/endocannabinoid-system
5. “Endocannabinoid System: Simple & Comprehensive Guide,” Leafly, April 3, 2023, https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system
6. “Phytocannabinoids: What Are They, and How Do They Work?” Leafwell, October 7, 2024, https://leafwell.com/blog/phytocannabinoids
7. “Cannabinoids and Pain: New Insights From Old Molecules,” Frontiers in Pharmacology, November 12, 2018, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.01259/full
8. “What Is the Interaction Between CBD and THC?” Healthline, January 24, 2024, https://www.healthline.com/health/the-entourage-effect
9. “How to stimulate the endocannabinoid system without cannabis,” Leafly, July 28, 2020, https://www.leafly.com/news/health/how-to-stimulate-the-endocannabinoid-system-without-cannabis
10. “Hiding in plain sight: The discovery of the endocannabinoid system,” International League Against Epilepsy, 2019, https://www.ilae.org/journals/epigraph/epigraph-vol-21-issue-1-winter-2019/hiding-in-plain-sight-the-discovery-of-the-endocannabinoid-system
This content is not intended as medical advice. The information provided is meant to encourage cannabis education, not replace direct patient-healthcare professional relationships. Always consult your primary care physician or other healthcare provider prior to using cannabis products for treatment of a medical condition. Any statements contained herein have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Products referenced are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Products are only available where consumption of cannabis is legal.


